
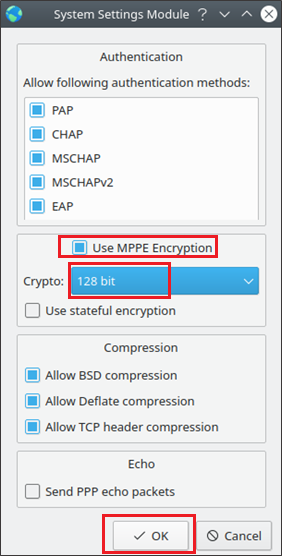
To resolve this issue, you can patch your /usr/bin/poff file by making the following changes on line 93: The reason for this is that the /usr/bin/poff script contains a bug when determining the PID of the specified pppd process if arguments were passed to pon. Note: The stop functionality of this script will not work if the updetach and persist arguments are passed to /usr/bin/pon when pon is started. Making A VPN Daemon and Connecting On Boot Make sure the script is executable and that the vpn table is added to /etc/iproute2/rt_tables 201 vpnĮxecute the following to disconnect from a VPN: Ip rule add fwmark 0x1 pri 100 lookup vpn Iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o $1 -j MASQUERADE Iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m multiport -dports 6667,6697 -j MARK -set-mark 0x1 Ip route add default via $5 dev $1 table vpn # This script is called with the following arguments:Įcho 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/$1/rp_filter etc/ppp/ip-up.d/01-routebyport.sh #!/bin/bash Note: All scripts in /etc/ppp/ip-up.d/ will called when the VPN connection is established. Omit \\ if your connection does not require a domain. Replace each bracketed term with an appropriate value. Make sure no one except root can read this file, as it contains sensitive information.Įdit the file. The /etc/ppp/chap-secrets file contains credentials for authenticating a tunnel. # (you may need to remove these refusals if the server is not using MPPE) # We won't do PAP, EAP, CHAP, or MSCHAP, but we will accept MSCHAP-V2 # Turn off compression protocols we know won't be used # We don't need the tunnel server to authenticate itself At a minimum, this file should contain the options lock, noauth, nobsdcomp and nodeflate. If you have trouble connecting to your network, you may need to relax the options. The /etc/ppp/options file sets security options for your VPN client. You can also edit all necessary configuration files by hand, rather than relying on pptpsetup.

You can #Connect after a tunnel has been configured. Pptpsetup -create my_tunnel -server -username alice -password foo -encrypt You can configure and delete tunnels by running the pptpsetup tool as root. You must also decide what to name the tunnel. This is not necessary for certain networks.
The authentication (Windows) domain name.The IP address or hostname of the VPN server.To configure pptpclient you will need to collect the following information from your network administrator:
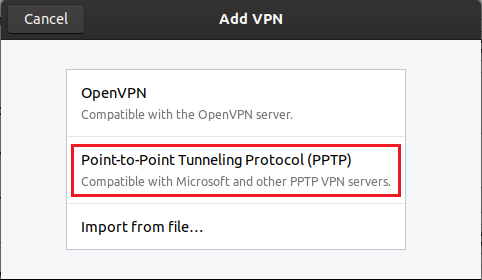
Warning: The PPTP protocol is inherently insecure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
